Ensuring the security of data sharing is crucial in a world where digital transactions and communications are the norm and the globe is becoming more interconnected. However, cyber risks continue to exist despite improvements in security protocols and encryption. One particularly pernicious and common type of cybercrime is the man-in-the-middle (MITM) assault. In this blog, we examine the methods, ramifications, and preventative tactics of the MITM attack in detail.
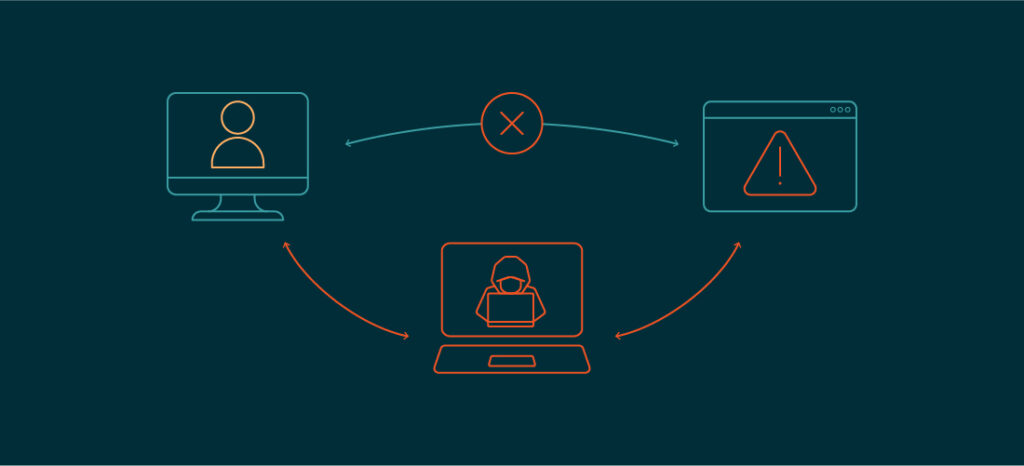
What is a Man-in-the-Middle Attack?
A man-in-the-middle attack is a form of cyberattack which occurs when a malevolent actor secretly eavesdrops on or intercepts communication between two parties with the intent to change or modify the data being shared. As an intermediary, the attacker can position himself thanks to this interception, which usually takes place without the communication parties’ knowledge or consent—hence the phrase “man-in-the-middle.”
Mechanisms of a Man-in-the-Middle Attack:
- Interception:
- By placing themselves in the way of the transmitter and recipient, the attacker is able to intercept data transmissions. Wi-Fi networks, Ethernet connections, and even hacked routers are just a few of the communication channels where this interception might happen.
- Eavesdropping:
- Once in place, the attacker can listen in on the conversation and obtain private messages, financial information, or login credentials, among other sensitive data. Then, this information may be used for nefarious activities like espionage, financial fraud, or identity theft.
- Modification:
- The transmitted data may occasionally be modified in addition to being intercepted by the attacker. An attacker can manipulate communication to their benefit by changing the substance of messages or transactions. For instance, they might add virus to downloaded files or change the payment information in a banking transaction.
Implications of a Man-in-the-Middle Attack:
The ramifications of a successful MITM attack can be severe, both for individuals and organizations:
- Data Breaches:
- MITM attacks have the ability to cause data breaches by granting unauthorized access to private information. Wide-ranging repercussions may result from this, such as monetary losses, harm to one’s reputation, and legal obligations.
- Identity Theft:
- Attackers can mimic people to carry out fraudulent actions including accessing bank accounts, making unlawful transactions, or committing cybercrimes in the victim’s name by intercepting login credentials or personal information.
- Compromised Security:
- MITM attacks compromise the security of online transactions, the exchange of sensitive information, and private discussions by undermining the integrity and confidentiality of communications. This damages cybersecurity initiatives and erodes user confidence in digital systems.
Prevention Strategies:
Preventing MITM attacks requires a multi-layered approach that addresses vulnerabilities at various stages of the communication process:
- Encryption:
- Implementing strong encryption protocols, such as HTTPS for web traffic or VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for network communications, can help secure data transmission, making it more difficult for attackers to intercept and decipher the exchanged information.
- Secure Authentication:
- Utilize secure authentication mechanisms, such as two-factor authentication (2FA) or biometric authentication, to verify the identities of communicating parties and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access to accounts or systems.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI):
- Deploy PKI solutions to establish secure communication channels and verify the authenticity of digital certificates. This helps prevent attackers from impersonating legitimate entities and conducting spoofing attacks.
- Regular Security Audits:
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and mitigate potential weaknesses in networks, systems, and applications. Promptly patching security vulnerabilities and staying abreast of emerging threats are essential for maintaining robust cybersecurity defenses.
- User Education:
- Raise awareness among users about the risks of MITM attacks and educate them on best practices for securely accessing and transmitting data online. Encourage vigilance against phishing attempts, suspicious links, and unsecured networks.
Conclusion
The security and integrity of digital communications are seriously threatened by the man-in-the-middle attack, necessitating proactive steps to successfully reduce the dangers. Individuals and businesses can protect their sensitive data in an increasingly linked world by defending against this ubiquitous threat, putting strong security measures in place, and cultivating a culture of cybersecurity awareness.
